Staking and PoS
Staking is the process of using cryptocurrency as a way of supporting the network of which it is native to. It is widely used on networks that adopt the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism or one of its variants. And as an incentive for maintaining the integrity of transactions on a particular PoS network rewards are received, this encourages token holders to therefore participate. For example Wanchain uses the Galaxy PoS mechanism and their native token Wancoin (WAN) can be used for staking to help govern the network. In return for this essential service a reward is received in the form of Wancoins ($WAN).
How Does Staking Work?
In a PoS network validators (nodes) essentially secure and govern the network thus playing a vital role. When validating transactions they are chosen in a random fashion based on both the number of coins they have committed (which also proves ownership) and the time those coins have been held for. They are then rewarded for attestations and any new blocks they produce and add to the blockchain. Rewards are in the form of new tokens which have been minted/forged as a result of this validation process. This encourages users to lock-up more of their token for longer so to have a greater chance of being selected and receive rewards in return for their services.
To ensure there are no bad validators in the space, PoS protocols have built-in mechanisms to penalize those who act maliciously or negligently when verifying transactions by “slashing” their activity. This effectively means a portion of their staked tokens (which is locked-in) will be lost and the participant ejected from the network. It is in the interest of validators to act honestly otherwise not doing so will have an adverse effect on the token price thus making their stakes depreciate in value. Validators are required to be online all the time, and any validators offline will still be penalized albeit not so severely.
In comparison to Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains such as Bitcoin, PoS does not require heavy computational power and the relevant hardware to go with it. This means PoS does not waste a lot of resources/energy and as no specialized mining equipment is needed PoS makes it easier for users to setup their own node for securing the network resulting in greater accessibility and decentralization. Ethereum currently uses PoW, but will be transitioning to a PoS protocol known as Casper in the near future thereby creating Ethereum 2.0. To become a validator on the Ethereum 2.0 blockchain you will need to stake 32 ETH which at today’s prices equates to approximately 6592 USD.
PoS staking systems also allow for delegation where an individual can delegate their voting rights and stake to a trusted 3rd party. Those delegates will then receive all of the rewards and transaction fees but pay their loyal supporters some of this in return for their vote. This makes it ideal for those users who wish to earn rewards without setting up and running a node. One well-known staking provider is InfinityStones and allows users to earn rewards from Wanchain, Cosmos, IoTeX as well as other networks. For a more detailed list of stakeable assets and their rewards please visit Staking Rewards.
Staking Marketcap
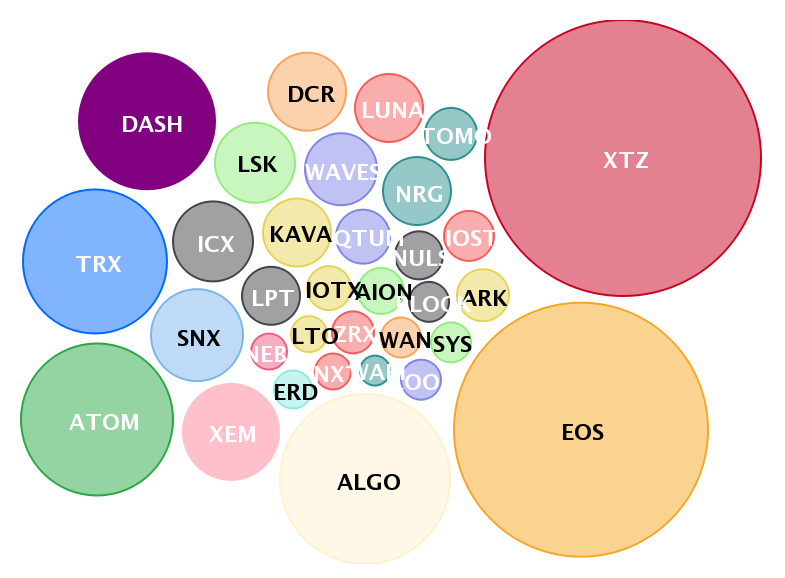
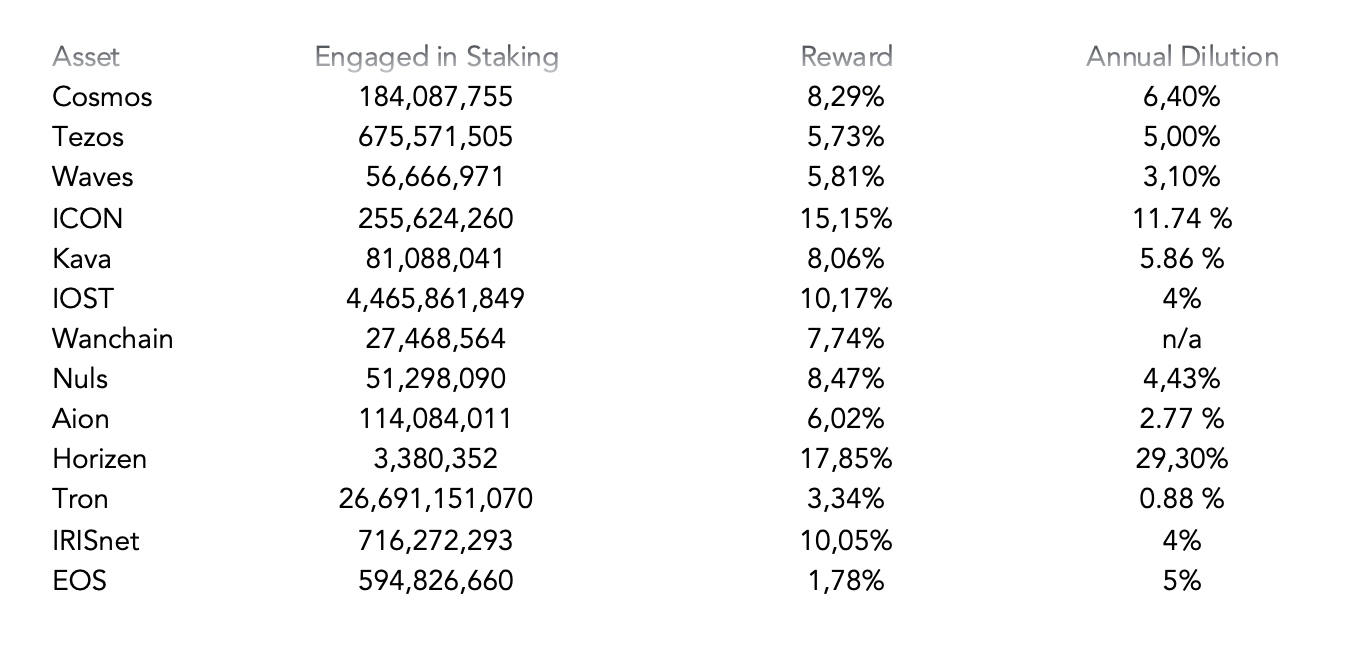
As of April 2020 here are the largest staking assets in terms of Marketcap. Tezos (XTZ), EOS and Algorand (ALGO) are the big 3. The Total Value Locked in staking was approximately $8.46 Billion with an average reward rate of 15.74%. Images courtesy of Staking Rewards
Getting Started
I have written an article on how to stake with Wanchain using their native coin Wancoin ($WAN) which can be conducted straight from their wallet making the whole process simpler than usual- Staking with Wanchain.
For more information about getting started with Staking please visit Staking Rewards. They have detailed lists of Staking Providers as well as guides and is a great place for doing more research.

