Wanchain
Today’s blockchain space is made up of a medley of technologies that are unable to talk with each other and thus remain isolated. Some of these unbridgeable networks can be public-to-public (Ethereum to Bitcoin), public-to-private (Ethereum-to-Enterprise), or private-to-private (Enterprise-to-Enterprise). This in turn will make it difficult for institutions and corporations to use due to incompatibilities between networks for the transferring of information and value. It will also make the case for a dependency on 3rd parties much more stronger which goes against the blockchain ethos.
Therefore to fully unlock the potential of blockchain technology and subsequent use cases there needs to be cross-blockchain communication and a common protocol for the transferring of information, and this is a gap in the market that Wanchain is actively working on in filling. Just how Wide Area Networks (WAN) connect Local Area Networks together, Wanchain is connecting isolated public and private networks for the greater good.
Technically speaking, Wanchain connects and exchanges value between different blockchain ledgers in a distributed manner, where It completes records of cross-chain transactions and maintains cross-chain transaction details. This then allows for the flow of digital assets and data globally through Wanchain’s cross-chain mechanism helping to create a truly Open Finance network. Security and privacy is at the forefront with the use of ring signatures in smart contracts and one-time address generation. Some of the cross-chain digital assets currently supported on Wanchain are:
How Wanchain Works
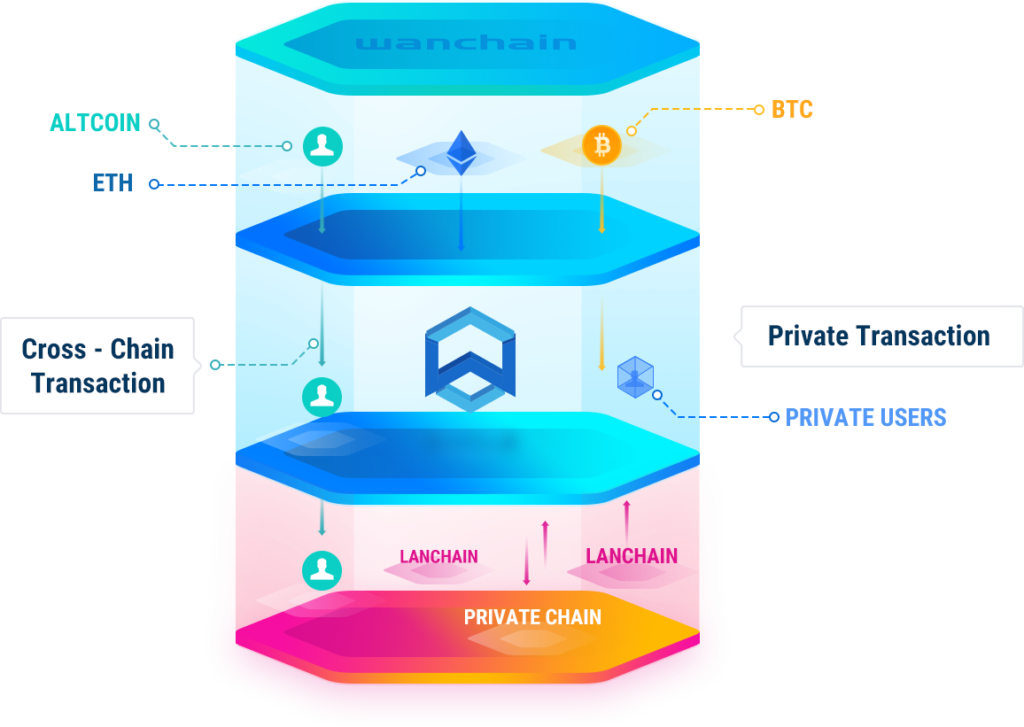
In blockchain terminology Interoperability is the ability of platforms to communicate with each other for the exchanging of information, and as mentioned previously this needs to be addressed in order for the whole sector to prosper. Wanchain’s cross-chain solution is to use specialized nodes also known as Storeman nodes, that employ a Secure Multi-Party Computation method (SMPC) with a threshold protected secret key to process cross-chain transactions.
SMPC is one of the core technologies underlying much of Wanchain’s powerful technology and allows for multiple parties to do part calculations on some data without revealing all the data to any one party making it highly secure. This then makes it especially useful when dealing with private keys which are used to secure cryptocurrencies such as WAN, BTC, ETH and others. SMPC allows for a group of decentralized nodes to create cryptocurrency transactions for a certain account without one node owner ever being able to gain access to the private key which controls that account, which is an important note.
For example, when executing a transaction from Ethereum to Wanchain the funds being sent from the Ethereum chain will be held in a locked account, while a corresponding amount WETH (Wanchain’s Ethereum mapping token) will be made available to the recipient after verifying the transaction has been confirmed on the original chain. The locked Ethereum is only made available again when the WETH holder sends that WETH to a Hashed Time Locked Contract (HTLC) account on Wanchain monitored by cross-chain Storemen nodes. At this point, the WETH is destroyed and the locked Ethereum is then released to the target Ethereum account.
Wanchain Applications
Wanchain touts the concept of Financial Inclusion where it seeks to give disadvantaged people and small enterprises worldwide better access to the financial system and low-cost financial services. 2.5 Billion people in the World are unable to access banks, open savings accounts or obtain credit and therefore remain separated from the global economy. Cross-border remittances through banks incur high fees. Ordinary investors can only buy relatively low-end financial products from banks and other FIs but cannot partake in early stage investments of technology companies such as Apple, Google and Alibaba before they get listed on stock exchanges. It is also difficult for many small to medium enterprises to obtain loan support from banks, despite good credit and outstanding performance, because they are not the target customers of traditional banks under the 80/20 rule.
Wanchain is thus aiming to become a distributed bank where different digital currencies and digital assets can be transferred in, transferred out and exchanged by blockchains. They are concentrating on building the financial infrastructure of the future which is based on digital assets and a distributed financial market which include:
Borrowing and Lending
Payment and Settlement
Transaction and Exchange
Investment and Financing
Tokenization of Traditional Assets
What is Wanchain 5.0?
Wanchain’s mission statement has always been to build an Open Financial ecosystem connecting traditional finance and assets to the World of decentralized finance. And by doing so will allow value to flow freely from different blockchains and between traditional ecosystems, where trustless applications can be built to capture this value, creating a value proposition for participants globally.
Wanchain 5.0 is the next step in bringing true interoperability between different heterogenous chains via the WAN Bridge standard. The WAN Bridge is an advancement of previous cross-chain implentations covering all the major aspects such as:
- Decentralization
- Trsutlessness
- Security
WAN bridges are also Universal meaning value can be transferred back and forth between any two connected chains. As more and more assets become interconnected, it is important that there is a distinction between the assets and the chain they reside on. Therefore Wanchain have come up with their own nomenclature for cross-chain tokens using the @ symbol and lowercase token symbol prefixes. For example, wanETH referes to the native asset ETH asset which has been issued as a wrapped token by Wanchain, it does not however denote which chain the token resides on. In order to do that, you would need to combine noclemclatures- wanETH@Wanchain or wanETH@EOS.
In addtion to the above, each WAN Bridge has a Storeman Group consisting of 21 Storeman Nodes- nodes that specifically manage the cross-chain value transfer process. And to ensure the safe and stable operation of the entire cross-chain system, Storeman Node operators must pledge a certain amount of collateral in the form of staking. WAN Bridges use a Threshold Signature Scheme combined with MultiParty Computation for guaranteeing the security of the locked assets and the smooth functioning of the cross-chain value transfer system. Cryptoeconomic incentives have also been implemented to guard against malicious behaviour. Node operators are required to over-collaterized the value of the cross-chain assets they issue, this way in case of any bad actors their collateral may be slashed. In this way, the cost of malicious behaviour is greater than the rewardsset to be gained by it, so Wanchain can ensure that node operators are always incentivized to behave honestly.
What is Wanchain 4.0?
As of now Wanchain’s latest version of its mainnet has reached version 4.0. This latest update was put live in Q1 2020 as per their roadmap, and incorporates the integration of private blockchains as well as a Trust-Bridge framework.
The T-Bridge framework is a genralised framework for data and asset transfer between public and private blockchains that do not share similar technical architectures otherwise known as Heterogeneous blockchains. As Wanchain 4.0 is focused more on supporting cross-chain interoperability between private and public blockchains, the T-Bridge framework was devised to help overcome the shortcomings of private to public cross-chain interoperability such as consensus mechanisms, privacy and security. The framework references architecture with modular components and common protocols. It also provides an extension of the Storeman nodes with additional support of the different SMPC algorithms. This framework can then be applied but not limited to:
- Customer Loyalty Points
- Insurance Claims
- Property Ownership Records and Loans
- The merging of TradFi and DeFi on a Global scale
- The rapid expansion of the Wanchain Cross-chain Network
- Cross-Chain Contracts
Companies such as Telfonica, PUC Berhad, Clubpass and Bitllywood are some that have already signed on to use WAN 4.0.
Wanchain Wallet
- Wancoin ($WAN)
- Bitcoin ($BTC)
- Ether ($ETH)
- EOS ($EOS)
- FinNexus token ($FNX)

How to Stake with $WAN
Now that you have $WAN in your Wanwallet, this can be used for Staking to earn rewards. Staking is the process of holding funds to receive rewards while contributing to the operations of a blockchain. As such, staking is widely used on networks that adopt the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism or one of its variants. Wanchain uses Galaxy Consensus PoS which is a protocol developed by the Wanchain team. In a PoS network, staking is used by validators to produce and validate new blocks. As opposed to Proof of Work (PoW) which is used by Bitcoin, PoS and more specifically Galaxy PoS, do not rely on heavy computational work but instead validators are selected randomly based on the number of coins they have committed to stake and its duration also known as Staking Power.
Wanchain makes the staking UX extremely easy and simple as it can be carried out directly through the Wanchain wallet where rewards will also be deposited. Within the wallet simply go to Galaxy PoS on the left-hand side menu bar and select Delegation. On the Delegation page select New Delegation (button on the right-hand side) which will bring up a pop-up window. On this window select the Validator you would like to delegate your stake to, select your Wanwallet address on the drop-down menu and enter the amount you wish to stake (the minimum being 100 WAN). On this window there are two other parameters to be aware of- First, the validator’s ‘Quota’ represents the amount of WAN that validator is able to accept in delegations. And the ‘Fee’ parameter- is the percent fee charged as commission by the validator. For example, if the network reward is 50 WAN and the fee is 15%, then you will receive 42.5 WAN as your reward, and 7.5 WAN will be paid to the validator.
Once you are happy with all the details click Next and lastly Send to confirm the transaction. As soon as the transaction has been confirmed on the network it will show under Delegation. The great thing about staking with Wanchain is that you can always top-up or withdraw your stake at anytime, both options can be found on the Delegation page. Please note when withdrawing your stake the transaction will be confirmed within 3 Epochs where your stake amount will go to zero and returned back into your Wanwallet.
Staking can also be conducted from the mobile wallet and can be monitored while being on the move, making it the first of its kind. When installing the mobile wallet ensure that you use the same seed phrase so that both the desktop light wallet and mobile wallet can be used in tandem.
With regards choosing a validator, there is a dedicated list detailing all the validators in the Wanchain ecosystem. This list can be found here- Validators List. You can then compare and select the appropriate validator as required. Otherwise another very useful website is- Wanstakeinsight.com which breaks down each Validator and also provides a guide on staking. It is important to note here that validators need to register themselves with Wanchain and require a certain amount of WAN to be pledged in a locked time smart contract in order to participate in the Wanchain ecosystem. This essential caveat aids in keeping the network secure by discouraging any bad validators in joining.
The staking process described above are for Delegators and is the simplest way to stake $WAN to earn rewards. You can run your own Validator node to earn more rewards but this is beyond the scope of this article due to the complexity of running such a node. If you wish to look into this yourself please visit the Wanchain website- Node Setup